Air and water pollution from agriculture in Europe
ESR 13 - Aslihan Ural
Wageningen University & Research (WUR)
In this study, WUR reserachers aim to better understand why air and water are polluted in Europe. Agriculture supports food security, however agriculture is also a pollution source, contributing emissions of nutrients to air and water. Researchers developed an integrated new model system to quantify nitrogen emissions to air and water, and river export of nitrogen and phosphorus by the basins in Europe. By soft-linking an agricultural nutrient emissions model (MITERRA-Europe) and a water quality model (MARINA-Global), we produced the new MITERRA-MARINA model focusing on agricultural production systems (see Figure 1). To this end, WUR researchers collaborate with the MITERRA model experts under the umbrella of Wageningen University & Research.
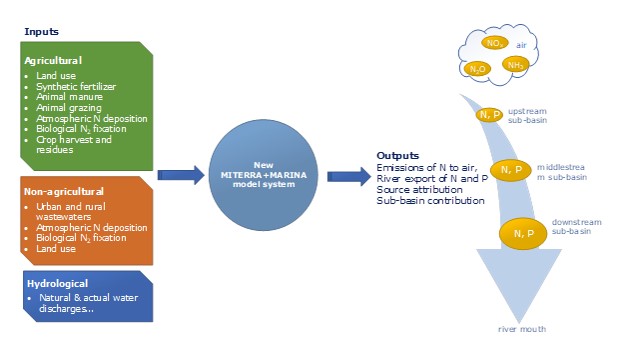
This model helps to better understand the causes of air and water pollution in a spatially explicit way. The model quantifies the source attribution of nitrogen and phosphorus exports from sub-basins and sectors (e.g., agriculture, urbanization). WUR researchers first quantify the current emissions in Europe, and later apply our model for various scenario analyses for the future including bio-based fertilizers (BBF) use. This will provide a better understanding of the environmental impacts of BBF in terms of nutrient pollution. This information could support effective agricultural management to reduce future air and water pollution.
